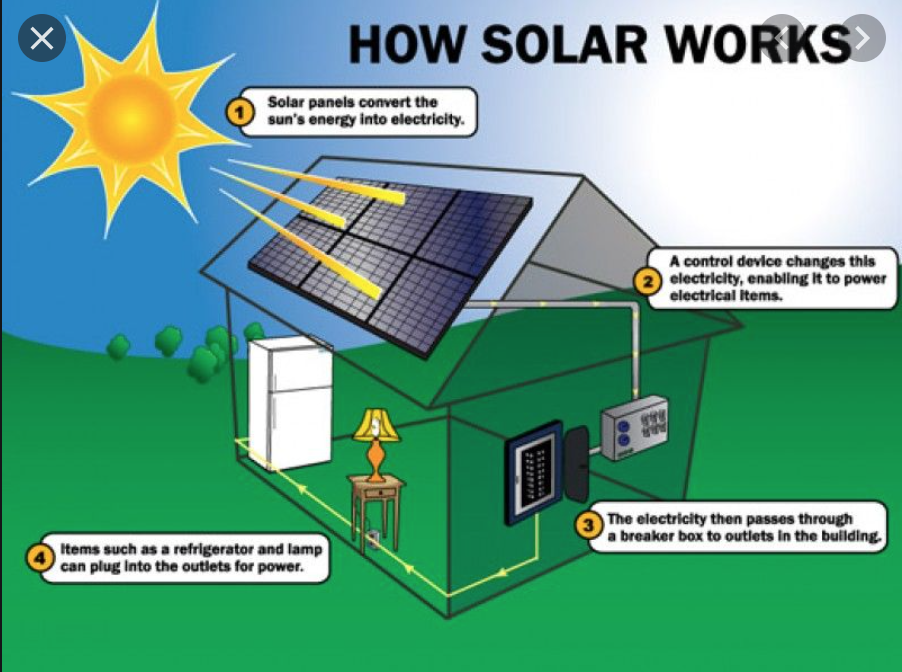
November 21st & 22nd, 2020 (Solar Energy, cont’d)
Problem Solving
—————————————————–
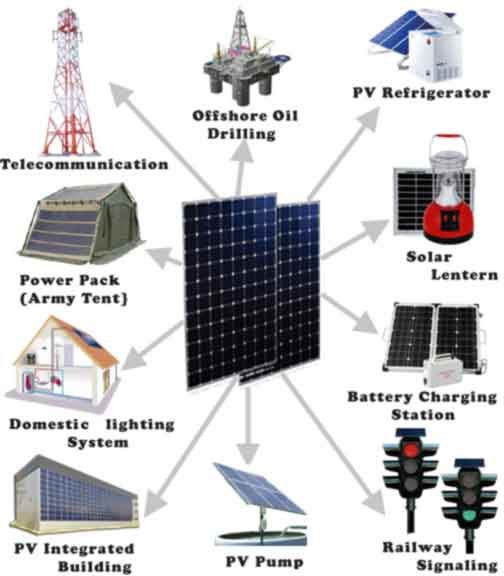
(Image 1.1)
Unit 2 Lesson 2- Solar Energy Application
ELA: Attentive Listening, Critical Listening (2) Maths: Sorting, Venn Diagrams (3) Science: Solar Energy
Electrical Current- a stream of charged particles, usually electrons, moving through an electrical conductor or space
Agrivoltaics- co-developing the same area of land for both solar photovoltaic power as well as for agriculture.
PV Tracker- A device that can track the position of the sun
Silicon- A chemical element classified as a semi-conductor that is used in most solar panels
Infrared Light- Light that comes from the sun which we can not see
Textiles- a type of cloth or woven fabric.
Molecule- a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction
Catalyst- any material that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed
Watch video on applications of Solar Energy
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XwFB22r9zRo
Complete these sentences based on the video:
- Less than _____ percent of the world’s electricity comes from Solar Power.
- Why would it not be a great idea to put solar panels in a hot climate (desert)?
- What steps could you take to make sure solar panels are working efficiently in a hot climate (desert)? The sun’s energy will not run out for billions of years.
- Solar windows convert only _____ percent of the sun’s energy to electricity.
- ______ is the most practical (best working) use for solar fabric.
- Solar Thermal Fuels turn the sun’s energy into ______.
- Swedish scientists were able to use solar thermal fuel to raise the temperature of an area by _____ degrees.
- How would you use two or more of these solar inventions (Agrovoltaics, PV Tracker, Solar Windows, Solar Thermal Fuels, Solar Fabrics)?
- How might these inventions be useful in your every day life?—————————————————————–
Okay Now lets create a Scratch Animation that demonstrates Solar Energy